The amount of spending on IoT equipment and factory automation has increased 14-fold as businesses prepare for Industry 4.0 and the advent of smart manufacturing

Automation and smart connected devices are part of digital transformation in the manufacturing industry
Smart manufacturing projects received more than $6.7bn (£5.26bn) in venture capital funding last year – as the dawn of Industry 4.0 looms.
The spending spike marks a 14-fold increase from 2013, according to the research from investment bank GP Bullhound.
The biggest market for smart manufacturing is currently Europe, which represents 30% of the global share.
European companies in the smart factories, IoT and digital design sectors are valued at a combined $24bn (£18.9bn) – ahead of the United States, which sits at $20bn (£15.72bn).
Dr Nikolas Westphal, director at GP Bullhound, said: “Europe’s smart manufacturing capabilities have undergone continuous growth, with an increased number of funding rounds and as an important consolidation target for US and Asian players.
“Smart manufacturing is the future and ultimately, we believe that automating repetitive tasks will enable us to concentrate on those qualities that set us apart from machines and algorithms: being and acting human.”
What is smart manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing refers to the trend towards using computer controls, modelling and big data to automate industrial processes.
The report describes it as the latest instalment of the “Smart Enterprise Wave”, and as a “defining” technological trend of today.
It differs from automation, which largely focused on robotics, in the fact that algorithms, AI and IoT allow for a more organised and intelligent factory floor – without the need for human intervention.
The report added: “While the old enterprise featured well-laid out, linear processes, the new enterprise focuses on agile, non-linear processes which are driven by big data analytics, constant monitoring and real-time collaboration.
“The defining feature of these new enterprises is the creation of platforms and the integration of concurrent technology trends.”
According to management consultancy firm McKinsey, smart manufacturing and the move to Industry 4.0 is predicted to create $2tn (£1.57tn) in value for manufacturers, by speeding up operations and making them more efficient.
What technologies are powering the move to Industry 4.0?
One of the key drivers for investment is the decline in cost for key Industry 4.0 technologies – lowering the barrier for entry for smaller manufacturing plants.
The number of installed IoT sensors, which allow different automated machinery to communicate with one another via the Internet of Things, is expected to top 75 billion by 2025.
The cost of one of these sensors has dropped from $40,000 (£31,450) in 2007 to $100 (£78.62) in 2014.
Similarly, the average cost per unit of industrial robots has decreased from $550,000 (£393,000) to $20,000 (£15,720) over the same period.
This is reflected in sales, with 387,000 industrial robots sold in 2017.
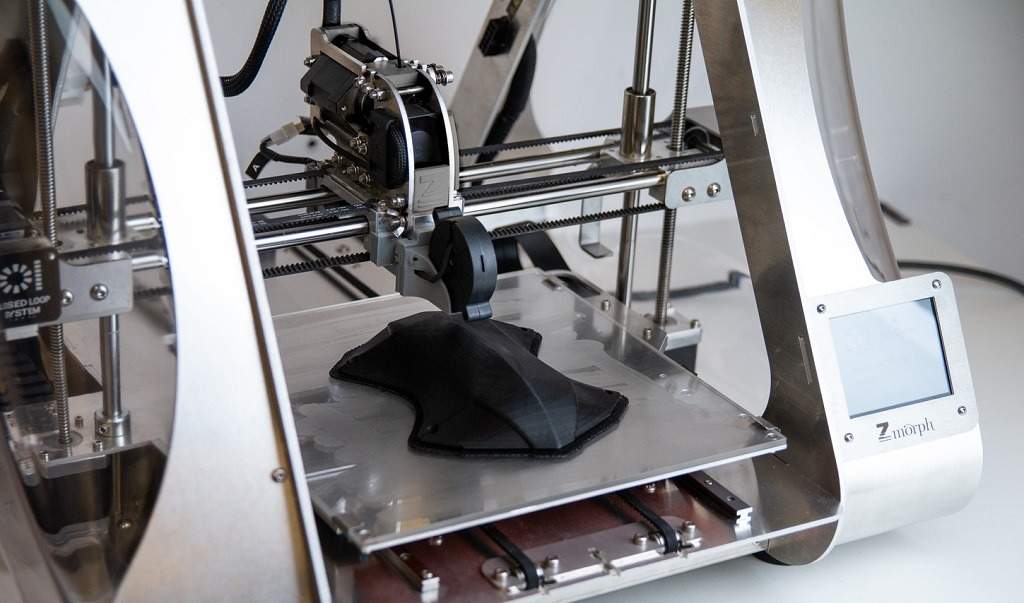

Another technology that is transforming the manufacturing sector is 3D printing, which is allowing companies to produce parts and fix equipment at a much faster rate than before.
The cost of 3D printing has seen a dramatic decline in cost too – $40,000 (£31,450) in 2007 to $100 (£78.62) in 2014 – and 6.7 million units are expected to be shipped by 2020.