The supercomputer is developed to speed up the digital biology revolution in the country
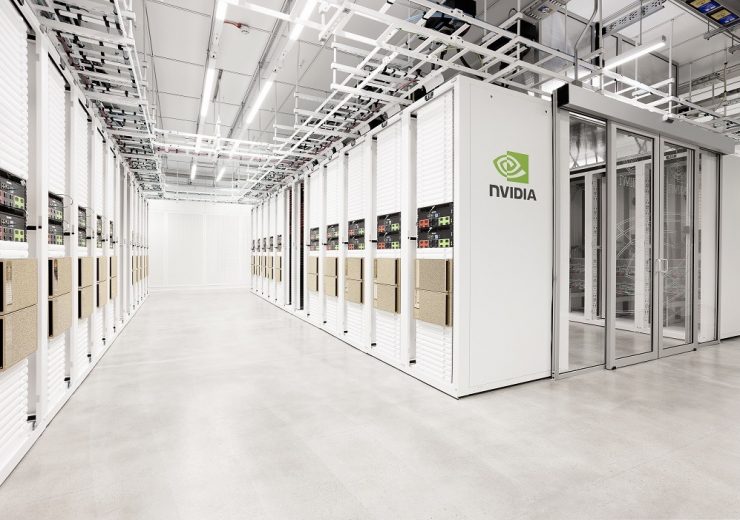

Cambridge-1 supercomputer is developed with an investment of $100m. (Credit: NVIDIA Corporation)
US technology company NVIDIA has launched a new supercomputer, known as Cambridge-1, to boost artificial intelligence (AI) and healthcare research in the UK.
Developed with an investment of $100m, the supercomputer is located at a facility operated by NVIDIA partner Kao Data.
Featuring 80 DGX A100 systems, Cambridge-1 is an NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD that has the ability to provide more than 400 petaflops of AI performance and 8 petaflops of Linpack performance.
NVIDIA said that the supercomputer is developed to enable UK scientists and healthcare experts to use a combination of AI and simulation to speed up the digital biology revolution.
Cambridge-1 will have its first projects with AstraZeneca, GSK, Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, King’s College London and Oxford Nanopore Technologies.
The projects are aimed at gaining an enhanced understanding of brain diseases and using AI to design new drugs. They will also focus on improving the accuracy of finding disease-causing variations in human genomes.
NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang said: “Cambridge-1 will empower world-leading researchers in business and academia with the ability to perform their life’s work on the U.K.’s most powerful supercomputer, unlocking clues to disease and treatments at a scale and speed previously impossible in the U.K.
“The discoveries developed on Cambridge-1 will take shape in the U.K., but the impact will be global, driving groundbreaking research that has the potential to benefit millions around the world.”
NVIDIA’s partnership with British-Swedish pharmaceutical AstraZeneca will focus on boosting drug discovery by creating a transformer-based generative AI model for chemical structures.
The collaboration has a separate project on Cambridge-1 focused on the use of AI in digital pathology.
The supercomputer is being used by King’s College London and Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust to teach AI models to produce synthetic brain images.
The synthetic data model will be used for an enhanced understanding of diseases like dementia, stroke, brain cancer and multiple sclerosis.
Oxford Nanopore utilises NVIDIA technology in various genomic sequencing platforms to create AI tools that improve the speed and accuracy of genomic analysis.
With the new NVIDIA’s supercomputer, the company is expected to reduce the duration of conducting tasks related to algorithm improvement to hours from days.